Is a college degree still worth it in the face of soaring costs and mounting student loan debts? College, a time-honored pathway to opportunity and success, now comes with a challenging financial reality. As tuitions climb and student loans become a common part of the college narrative, understanding this new financial terrain is more important than ever.
For students dreaming of their future and parents supporting those dreams, this changing landscape can seem daunting.
How do you balance the pursuit of higher education with the reality of financial burdens that could last for years? Is the investment in a college degree still a smart choice when weighed against the debt it often requires? And what strategies can families and students use to navigate these financial waters wisely?
This article dives into these critical questions, aiming to provide a broad overview of investing in a college degree in today’s economic context. We’ll explore the financial trends in higher education, examine the long-term effects of student loans, and provide practical advice for making informed decisions.
Whether you’re a student plotting your educational journey or a parent guiding your child through these decisions, join us in uncovering how to make the most of college in an era of rising student loans.
The Rising Tide of Student Loan Debt
In recent years, the narrative of the American dream has increasingly been woven with threads of student loan debt. It’s a story familiar to many families: the pursuit of higher education as a gateway to opportunity, now shadowed by the burden of financial obligations.
As of 2023, student loan debt in the United States stands as a colossal figure, surpassing $1.7 trillion. This staggering amount affects over 44 million borrowers, making it the second-highest consumer debt category, only behind residential real estate debt. These numbers aren’t just statistics; they represent real challenges for students and families navigating the world of higher education.
This debt landscape has evolved dramatically. Two decades ago, student loans were a less dominant aspect of financing education. Now, they are a pivotal part of the college experience for many. The average debt per student stands at around $30,000, with many facing much higher amounts. This shift is not just about rising tuition costs; it reflects a fundamental change in how society funds higher education.
Federal and state funding cuts have shifted much of the cost of college onto students and their families. As a result, loans have become an essential tool for accessing higher education, particularly for middle and lower-income families. This shift raises crucial questions about the long-term impact on financial well-being and economic mobility.
Graduates entering the workforce with substantial debt face challenges in achieving financial milestones, such as buying a home or saving for retirement. Moreover, the burden of debt can influence career choices, pushing graduates towards higher-paying jobs, sometimes at the expense of their passions or callings.
Student loan debt also has broader societal implications. It impacts consumer spending and economic growth and is a source of significant stress and anxiety for borrowers. The ripple effects extend through families and communities, contributing to wider economic and social consequences.
As students and parents, understanding this landscape is critical. It’s not just about recognizing the challenge but also about being informed and prepared. Navigating student loan debt requires careful planning, understanding of available options, and strategic decision-making.
In the following sections, we will explore strategies for managing this debt and making informed choices about higher education. The goal is not just to cope with the reality of student loan debt but to thrive despite it, making informed decisions that balance educational aspirations with financial prudence.
Related: Boost Savings with New Retirement Plans for Student Loans
Related: Top 12 No-Loan Colleges with Amazing Aid Packages
Understanding the Different Types of Student Loans: Federal and Private Options
There are several types of student loans, mainly categorized into federal and private loans:
- Federal Student Loans: These are loans provided by the government with fixed interest rates and more flexible repayment terms. They include:
- Direct Subsidized Loans: For undergraduate students with financial need; the government pays the interest while the student is in school.
- Direct Unsubsidized Loans: Available to undergraduate, graduate, and professional students; no requirement to demonstrate financial need.
- Direct PLUS Loans: For graduate or professional students and parents of dependent undergraduate students; requires a credit check.
- Direct Consolidation Loans: Allows students to combine multiple federal education loans into one loan at no cost.
- Private Student Loans: Offered by banks, credit unions, and other financial institutions, these loans are not backed by the government. Their terms, interest rates, and eligibility criteria are set by the lenders and can vary significantly.
Each type of loan has its own set of terms, conditions, and eligibility criteria. It’s important for borrowers to understand these differences when choosing the best loan for their education financing needs.
Assessing the Value of a College Degree
For generations, a college degree has been seen as a golden ticket to success, a pathway leading to greater career opportunities, higher earnings, and a more secure future. But as the landscape of higher education shifts, many students and parents are questioning this long-held belief. Is a college degree still worth the investment in today’s world?
Historically, the value of a college degree was almost unquestionable. College graduates, on average, have consistently earned more than those without a degree, leading to a widespread perception that higher education is a surefire investment in one’s future. However, as tuition costs soar and student loan debt mounts, the calculation of this value has become more complex.

The financial aspect is often the most tangible measure of a college degree’s worth. Statistics show that, on average, college graduates earn significantly more over their lifetime compared to those with only a high school diploma. This “earnings premium” is a key factor in evaluating the return on investment for a college education. But it’s not just about earnings. The rate of employment, the kind of careers accessible to graduates, and opportunities for career advancement also play crucial roles.
In assessing the value of a college degree, one must consider employment rates for graduates. A degree in a field with high demand and low supply can open doors to lucrative and stable career paths. Conversely, degrees in oversaturated fields might not offer the same return. Thus, the choice of major and the current job market trends are critical considerations.
Moreover, a college degree often extends beyond just financial gains. It can be a gateway to personal development, broader worldviews, and networking opportunities that can be invaluable in one’s career and personal life. The experience of college itself, with its diverse social and learning environments, can foster critical thinking, adaptability, and other soft skills that are highly valued in the job market.
However, it’s also important to acknowledge that the traditional four-year college route may not be the best fit for everyone. In recent years, there has been a growing appreciation for vocational training, apprenticeships, and other forms of education that can lead to rewarding careers without the need for a traditional college degree.
While the value of a college degree remains significant, it’s more important than ever for students and their families to make informed, strategic decisions about higher education. This means considering personal interests, market trends, financial implications, and alternative educational pathways.
Many books provide students with a treasure trove of knowledge regarding money and finances. Here is a list of 9 books that can help elevate student’s knowledge concerning money and finances.
The goal is to find a balance that aligns educational aspirations with practical, real-world outcomes, ensuring that the investment in higher education pays off in the long run.
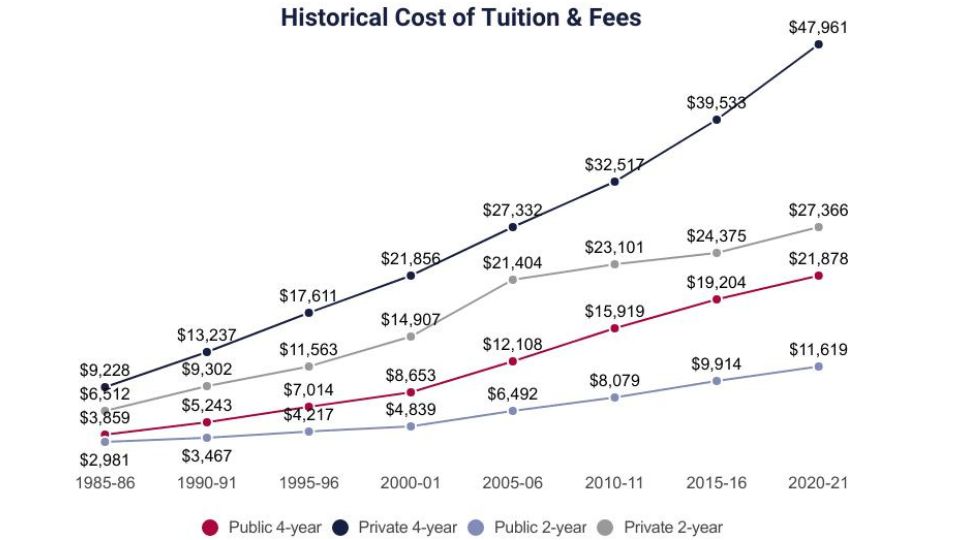
The Real Cost of Higher Education
For families navigating the journey of higher education, understanding the real cost of a college degree is crucial. It’s not just the tuition fee that counts; several other expenses add up, impacting the family budget significantly.
Tuition is the most apparent expense, varying widely between public and private institutions. But beyond this, there are costs like room and board, books and supplies, transportation, and personal expenses. Living expenses can vary dramatically depending on the location of the college.
Then there are opportunity costs—the income a student forgoes to attend school full-time. These are often overlooked but crucial for understanding the total financial impact of a college education.

Financial aid can significantly reduce this burden. Scholarships and grants, which don’t need to be repaid, can be lifesavers. They might be merit-based, need-based, or specific to fields of study or demographics. Loans, on the other hand, need careful consideration due to their long-term implications. Federal student loans typically offer more favorable terms and protections compared to private loans.
Understanding and planning for these costs is key to making informed decisions about higher education, ensuring that the investment aligns with future financial goals and capabilities.
Related: How the 2024 FAFSA Delays Threaten Student Futures
Strategies for Managing Student Loan Debt
Navigating the world of student loans can be daunting, but with the right strategies, managing this debt becomes more manageable. It starts with making informed choices about which loans to take. Federal loans often offer more favorable terms and protections than private loans, including income-driven repayment plans and potential for forgiveness.
Once in repayment, budgeting is crucial. Allocating funds towards student loan payments as a priority can help avoid late fees and additional interest. For those struggling, exploring income-driven repayment plans can adjust monthly payments according to income, providing much-needed relief.
Refinancing can be a smart move for some, potentially lowering interest rates and monthly payments. However, it’s important to understand that refinancing federal loans with a private lender means losing federal protections and benefits.
Lastly, investigate loan forgiveness programs. Programs like Public Service Loan Forgiveness offer a path to loan forgiveness for those in qualifying public service jobs, but they require strict adherence to their terms. Being proactive and informed is key to successfully managing student loan debt.
Related: Cosigning Your Child’s Student Loan: Can it Unlock Their Future?
Making Informed Decisions About Student Loan Debt
As we wrap up our exploration of the intricate world of higher education and student loans, it’s clear that this journey requires careful consideration and informed decision-making.
From understanding the rising tide of student loan debt to assessing the value of a college degree, every step calls for thoughtful analysis. We’ve seen how the real cost of higher education extends beyond tuition, encompassing a range of direct and indirect expenses, and we’ve delved into effective strategies for managing student loan debt, emphasizing the importance of budgeting, refinancing options, and loan forgiveness programs.
Remember, the path to higher education is as unique as the individual embarking on it. By staying informed and planning carefully, students and their families can navigate this path with confidence, ensuring that the investment in education is both rewarding and sustainable.
Additional Resources
Here are three of the most important sites offering comprehensive information about student loans:
- Federal Student Aid Information Center | USAGov
- Website: Federal Student Aid Information Center
- Features: Provides information on more than $125 billion in federal grants, work-study, and loans for students. Includes contact details for queries and assistance related to federal student aid.
- U.S. Department of Education – Financial Aid
- Website: Financial Aid – ED.gov
- Features: Offers comprehensive information on financial aid for college, including details on avoiding scams, sources of aid, FAFSA, and tools for estimating college costs. Also provides information on repaying student loans and resources for aid professionals.
- Federal Student Aid (studentaid.gov)
- Website: Federal Student Aid
- Features: This is the official site for accessing and managing federal student aid. It offers tools like Loan Simulator, information on different loan types, and detailed guides on the process of applying for and managing student loans.
These websites are essential resources for anyone seeking to understand student loans, offering a wealth of information on applying for aid, loan management, repayment options, and forgiveness programs.





